
Student Projects
VE/VM450

Manufacturing and Testing of Lab-scale Non-pneumatic Wheels
Instructors: Prof. Mingjian Li
Team Members: Houfu Jiang, Zihe Liang, Pengyu Xu, Dongjie Yan, Claudia Jorda Terrado
Project Video
Team Members

Team Members:
Houfu Jiang, Zihe Liang, Pengyu Xu, Dongjie Yan, Claudia Jorda Terrado
Instructors:
Prof. Mingjian Li
Project Description
Problem Statement
Non-pneumatic wheel(NPW) is a field that is gaining interest of study in many applications. NPW can replace traditional wheels in conditions in which pneumatic wheels could leak or blow out. Our project aims to manufacture lab-scale NPWs and test manufactured wheels.

Fig. 1 Non-pneumatic wheel manufactured through injection molding
Concept Generation
Injection molding is chosen due to manufacturing time and resolution. Mold design is important in injection molding, therefore an injection mold for NPW is developed as concept in manufacturing. Non-pneumatic wheels need to be able to deform and resist high loads, torsion and abrasion, therefore TPU is chosen as material. Moreover, properties of manufactured wheels need to be determined, so self-designed testing platform is chosen to be developed.
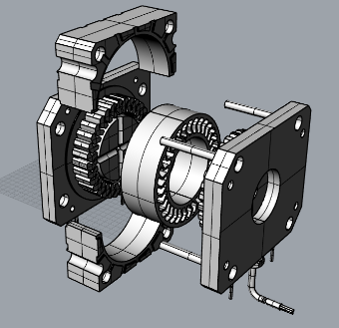
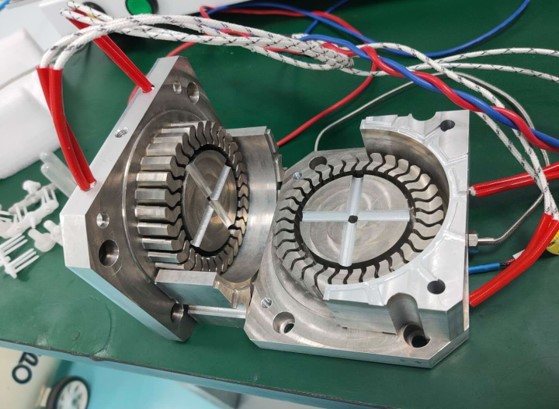
Fig. 2 Wheel injection mold

Fig. 3 Flow chart of the project
Design Description
The mold used to manufacture NPW has been designed according to the engineering specifications and requirements. A testing platform has been designed so that friction of the wheel can be measured, and thus calculated the longitudinal, lateral and vertical stiffnesses. To manufacture tensile test specimens that allow testing of the material, an injection mold has been designed and fabricated. Specimens are injected and tested through a tensile test.
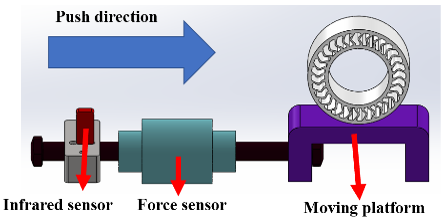
Fig. 4 Wheel testing platform setup
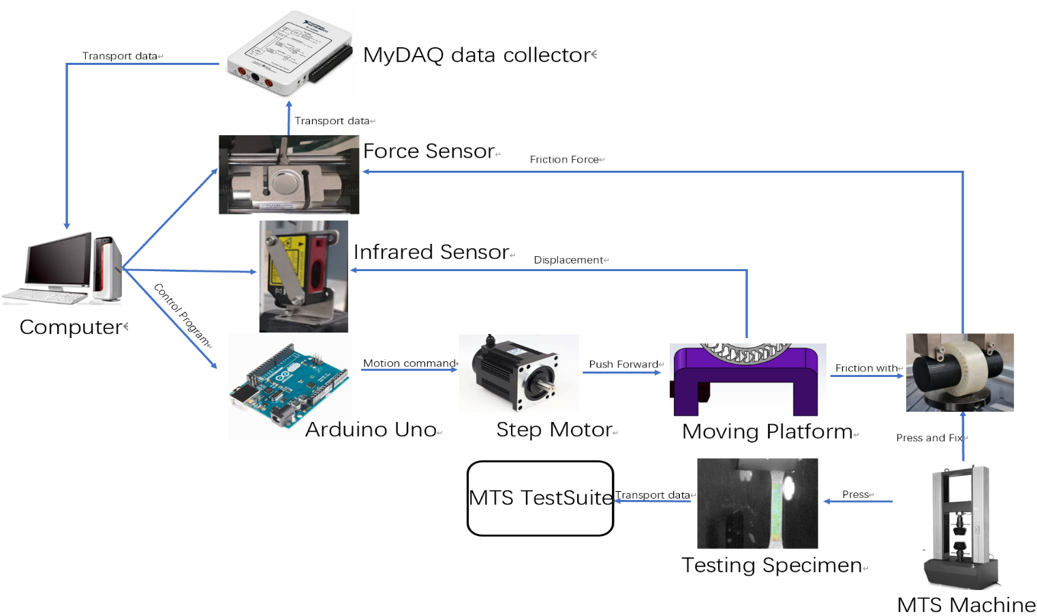
Fig.5 Wheel testing concept
Modeling and Analysis
As for the wheel, the friction is tested by applying a load on it, while the platform that the wheel is resting on is moving. The stiffness is tested by applying a load on the wheel and observing its deformation. The material specimen is tested through a tensile test.
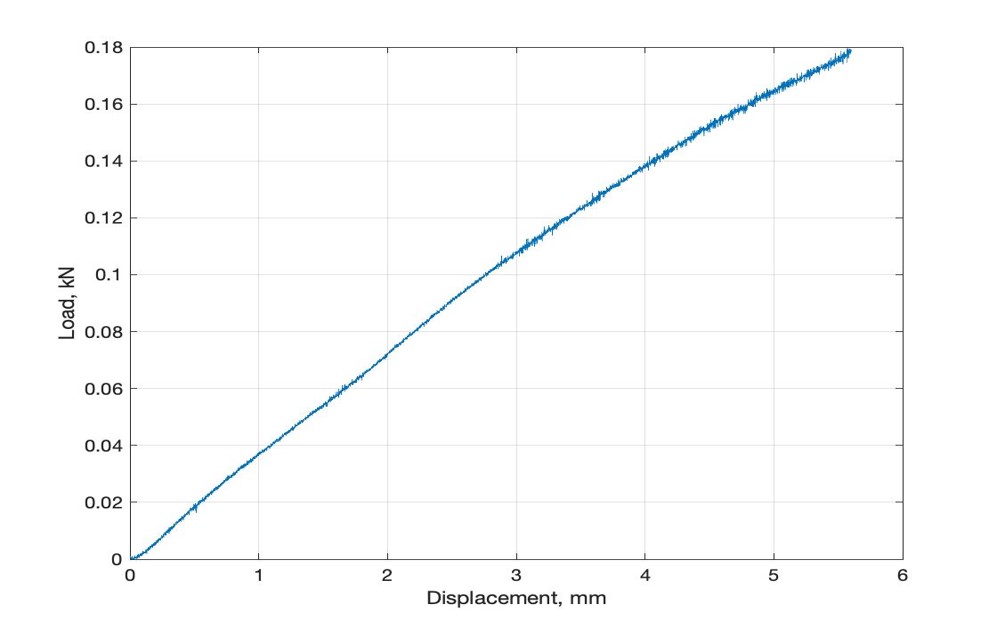
Fig. 6 Vertical stiffness test of NPW
Validation
Validation Process:
As for manufacturing, injected wheel is processed to eliminate sprue, get deburred and weighed to compare with engineering specified weight. A mass ratio is calculated and thus the mold filling factor. As for testing, videos of testing are shot to show testing degree of freedom and one maximum displacement test is conducted to measure range of our testing platform.
Other specifications can also be verified using easy experiments.
Validation Results:
√ Manufacturing time<=0.5hr √ Weight of wheel≈72.7g √ Mold filling factor>=95%
√ Testing range>=20mm
√ Degree of freedom=3
√ Resolution<=0.01mm √ Total cost<=6000RMB √ means having been verified
As for manufacturing, injected wheel is processed to eliminate sprue, get deburred and weighed to compare with engineering specified weight. A mass ratio is calculated and thus the mold filling factor. As for testing, videos of testing are shot to show testing degree of freedom and one maximum displacement test is conducted to measure range of our testing platform.
Other specifications can also be verified using easy experiments.
Validation Results:
√ Manufacturing time<=0.5hr √ Weight of wheel≈72.7g √ Mold filling factor>=95%
√ Testing range>=20mm
√ Degree of freedom=3
√ Resolution<=0.01mm √ Total cost<=6000RMB √ means having been verified
Conclusion
Non-pneumatic wheels are injected out of TPU and manufactured using injection molding. The properties of the material were analyzed through a tensile test while the stiffness and friction of the wheel were tested in a testing platform designed by the team that is inexpensive and specifically for lab-scale wheels. We were able to design injection molds and testing platform, and fulfill the customer requirements.
Acknowledgement
Sponsor: Ju Jaehyung S-Lab
Li Mingjian from UM-SJTU Joint Institute
Li Mingjian from UM-SJTU Joint Institute
Reference
[1] Pajtas, Scott R. “Polyurethane Non-Pneumatic Tire Technology-Development and Testing History.” SAE Transactions, vol. 99, 1990, pp. 1094–1108.
[2] Groover. “Fundamentals of modern manufacturing”, 4th edition. 2010, pp. 209.
[2] Groover. “Fundamentals of modern manufacturing”, 4th edition. 2010, pp. 209.
UM-SJTU JOINT INSTITUTE